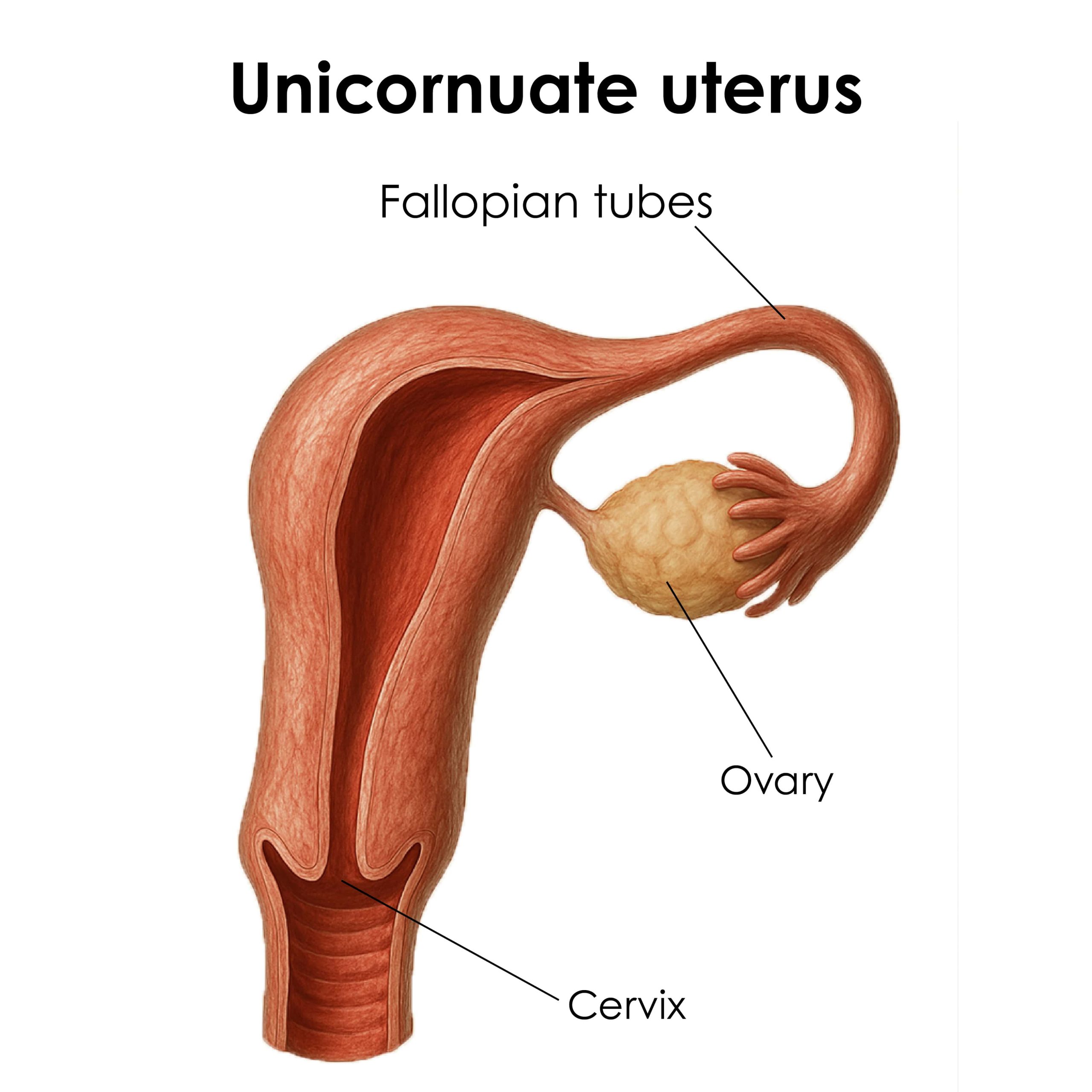
Unicornuate Uterus
This condition occurs when only one side of the uterus forms, resulting in a smaller, single-sided cavity.
Impact on Fertility and Pregnancy:
Increased risk of miscarriage, preterm birth, and complications during delivery.
Some women have a non-functional hemi-uterus, which can cause pain due to trapped menstrual blood.
Treatment
Surgical removal of a non-functional hemi-uterus and tailored fertility care.
Didelphys Uterus
This rare anomaly occurs when two separate uterine cavities form due to incomplete fusion of the reproductive system during fetal development.
Impact on Fertility and Pregnancy:
Potential for recurrent miscarriage, abnormal positioning of the fetus, or difficulties during delivery.
Treatment
Surgical correction or fertility treatments depending on the patient’s specific condition.
Fibroids and Polyps
Acquired anomalies like uterine fibroids (non-cancerous growths) or polyps (growths in the uterine lining) can interfere with embryo implantation or pregnancy maintenance.
Impact on Fertility and Pregnancy:
Difficulty conceiving, recurrent miscarriage, or complications like heavy bleeding during pregnancy.
Treatment
Removal through hysteroscopy or laparoscopy to enhance uterine function.