Uterine and Tubal Assessments
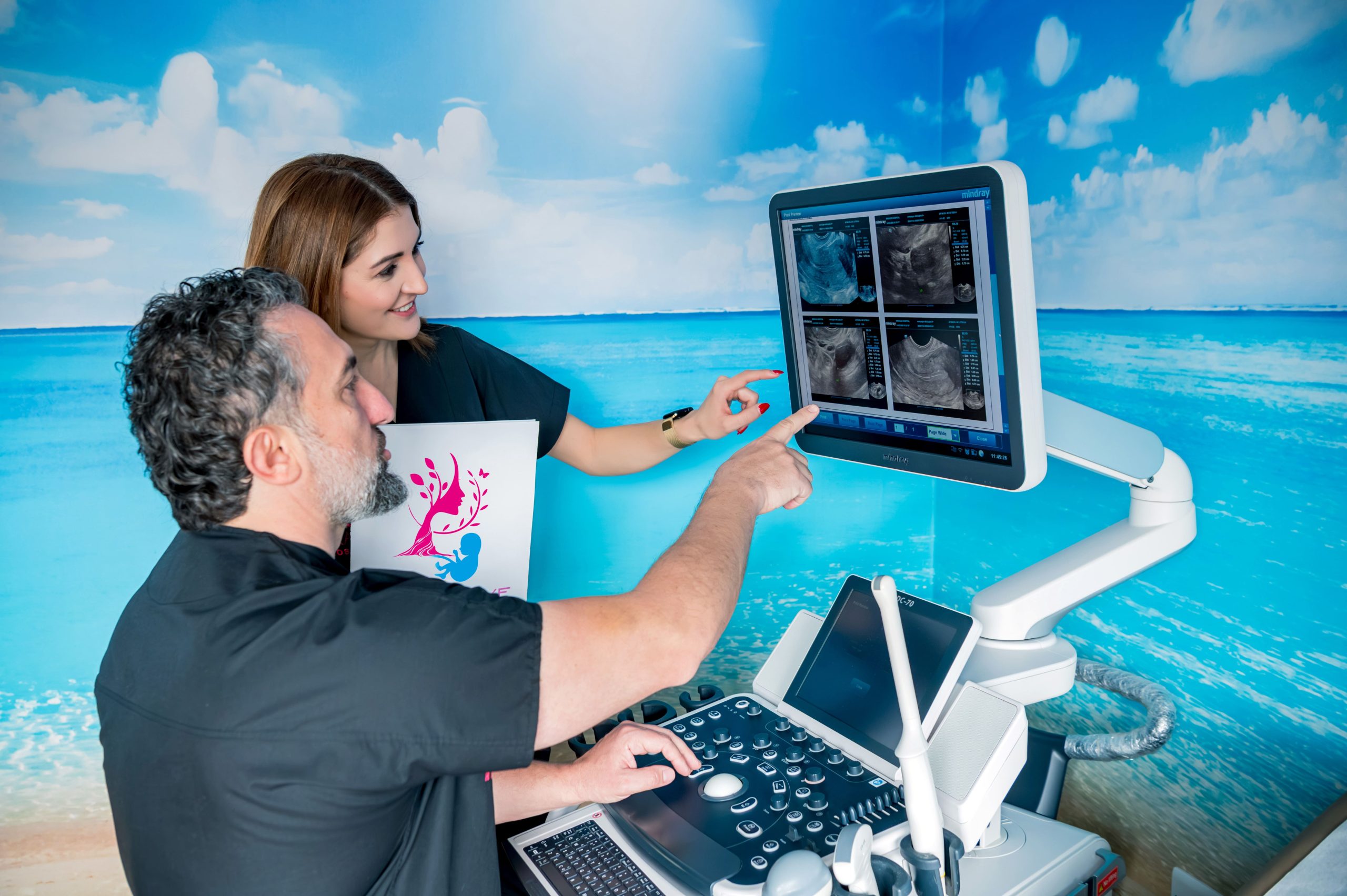
Transvaginal Ultrasounds: Detect structural issues like fibroids, polyps, or cysts.
Hysterosalpingogram (HSG): An X-ray test to check for tubal blockages and assess the uterine cavity.
Sonohysterogram: Combines ultrasound with saline infusion to evaluate the uterine lining.
Hysteroscopy: A minimally invasive procedure using a small camera to inspect and correct uterine abnormalities.
Hormonal Testing
Tests Include Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH), estradiol, FSH, luteinizing hormone (LH), and thyroid function tests.
Objective: Identifies hormonal imbalances that may affect ovulation and overall fertility.
Diagnostic Laparoscopy
Purpose: Examines the pelvic organs to detect endometriosis, adhesions, or other abnormalities.
Benefits: Provides both diagnostic insights and the ability to perform corrective procedures simultaneously.