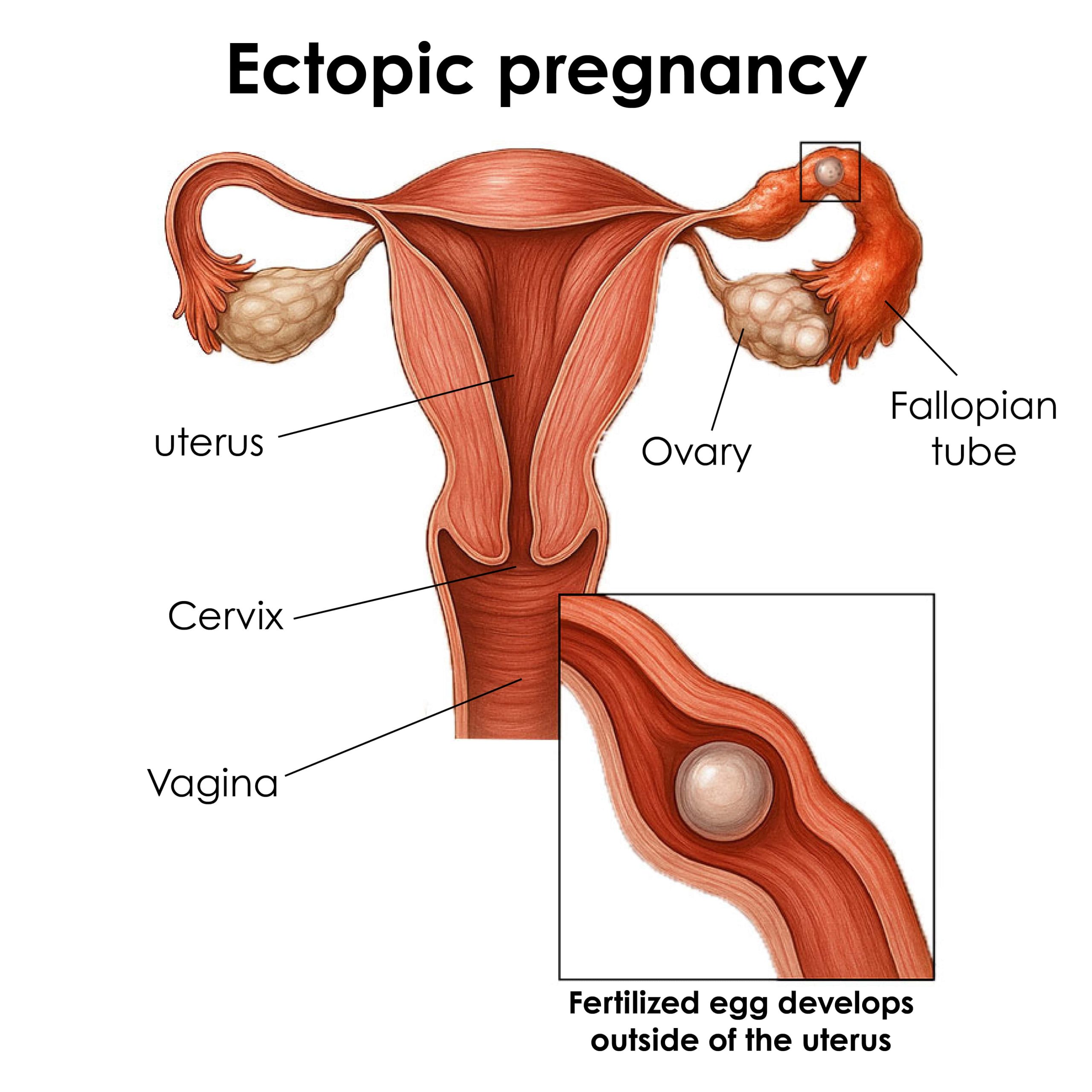
DefinitionAn
ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the uterus, most commonly in the fallopian tube (tubal pregnancy).
FrequencyEctopic pregnancies occur in about 1 in 50 pregnancies, making early detection and intervention critical.
SymptomsSigns include pelvic pain, light vaginal bleeding, and abdominal discomfort. Severe cases may involve shoulder pain, dizziness, or fainting.
Risk FactorsPrevious ectopic pregnancies, pelvic infections, endometriosis, smoking, or prior abdominal surgeries increase the risk.
TreatmentEctopic pregnancies require immediate medical attention, as they cannot result in a viable pregnancy. Treatments include medication or surgery.